Doing things right vs. doing the right things
The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic shocked the world with its rapid spread despite stringent containment efforts, and it continues to wreak havoc. The surrounding uncertainty due to the novelty of this virus has prompted significant investigation to determine proper containment, treatment, and eradication efforts.1,2 In addition, health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and a shortage of resources resulting in lower quality care for patients and putting health care workers (HCWs) at risk for infection.3,4
While there is a lot of emerging clinical and basic science research in this area, there has been inconsistent guidance in regard to the containment and prevention of spread in health care systems. An initiative to minimize HCW exposure risk and to provide the highest quality care to patients was implemented by the Section of Hospital Medicine at our large academic medical center. We used a hospital medicine medical-surgical unit and converted it into a Person Under Investigation (PUI) unit for patients suspected of COVID-19.
Unit goals
- Deliver dedicated, comprehensive, and high-quality care to our PUI patients suspected of COVID-19.
- Minimize cross contamination with healthy patients on other hospital units.
- Provide clear and direct communications with our HCWs.
- Educate HCWs on optimal donning and doffing techniques.
- Minimize our HCW exposure risk.
- Efficiently use our personal protective equipment (PPE) supply.
Unit and team characteristics
We used a preexisting 24-bed hospital medicine medical-surgical unit with a dyad rounding model of an attending physician and advanced practice provider (APP). Other team members include a designated care coordinator (social worker/case manager), pharmacist, respiratory therapist, physical/occupational therapist, speech language pathologist, unit medical director, and nurse manager. A daily multidisciplinary huddle with all the team members was held to discuss the care of the PUI patients.
Administrative leadership
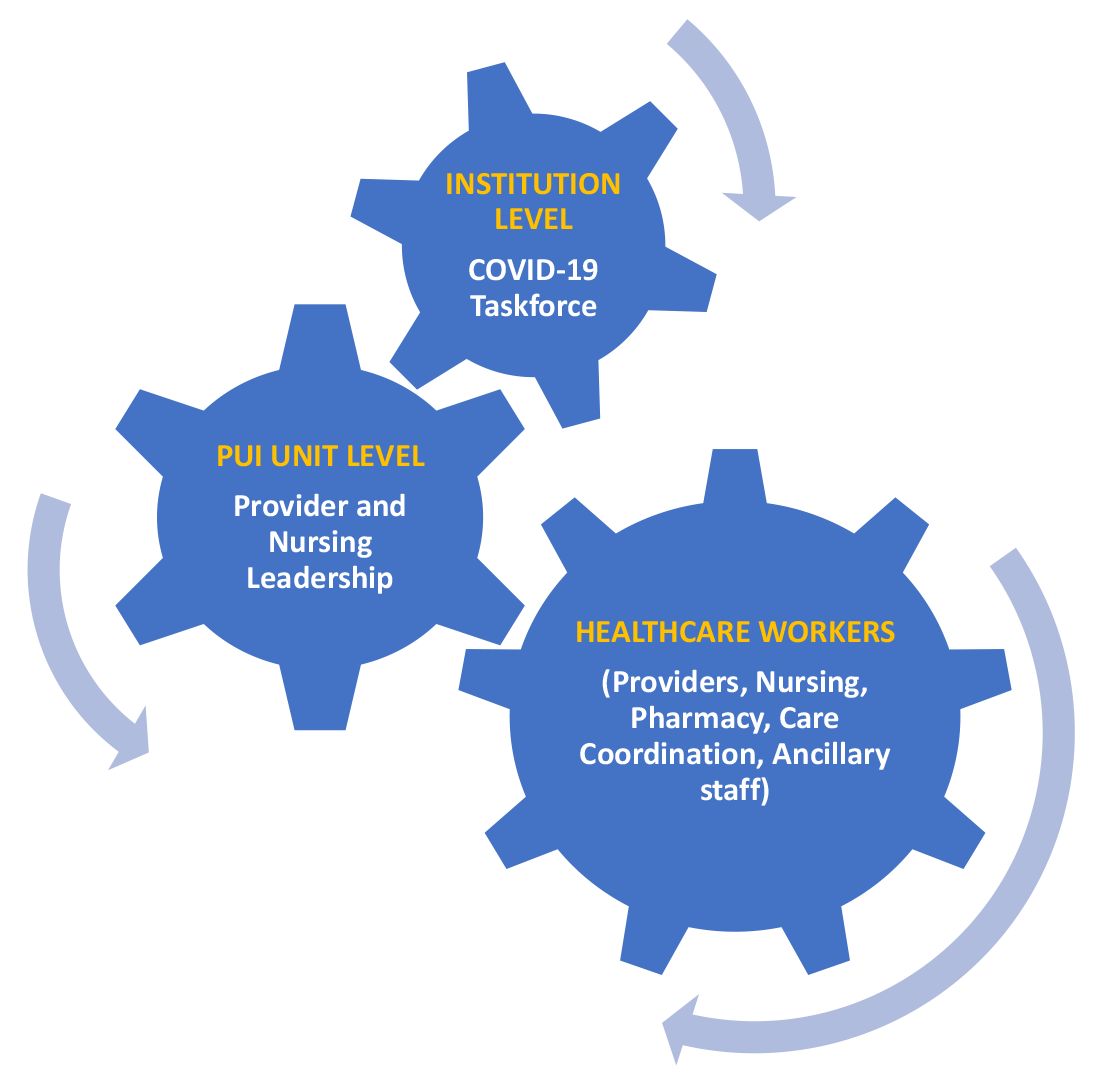
A COVID-19 task force composed of the medical director of clinical operations from the Section of Hospital Medicine, infectious disease, infection prevention, and several other important stakeholders conducted a daily conference call. This call allowed for the dissemination of information, including any treatment updates based on literature review or care processes. This information was then relayed to the HCWs following the meeting through the PUI unit medical director and nurse manager, who also facilitated feedback from the HCWs to the COVID-19 task force during the daily conference call. (See Figure 1.)
Patient flow
Hospital medicine was designated as the default service for all PUI patients suspected of COVID-19 and confirmed COVID-19 cases requiring hospitalization. These patients were admitted to this PUI unit directly from the emergency department (ED), or as transfers from outside institutions with assistance from our patient placement specialist team. Those patients admitted from our ED were tested for COVID-19 prior to arriving on the unit. Other suspected COVID-19 patients arriving as transfers from outside institutions were screened by the patient placement specialist team asking the following questions about the patient: