It’s noon on Tuesday, and James, a new PGY-2 resident, begins his presentation on COPD. After five minutes, you notice half of the residents playing Words with Friends, the “ortho-bound” medical student talking with a buddy in the back, and the attendings looking on with innate skepticism.
Your talk on atrial fibrillation is next month, and just watching James brings on palpitations of your own. So what do you do?
Introduction
Public speaking is a near certainty for most of us regardless of training stage. A well-executed presentation establishes the clinician as an institutional authority, adroitly educating anyone around you.
So how can you deliver that killer update on atrial fibrillation? Here, we provide you with 10 tips for preparing and delivering a great presentation.
Preparation
1. Consider the audience and what they already know. No matter how interesting we think we are, if we don’t present with the audience’s needs in mind, we might as well be talking to an empty room. Consider what the audience may or may not know about the topic; this allows you to decide whether to give a comprehensive didactic on atrial fibrillation for trainees or an anticoagulation update for cardiologists. Great presenters survey their audience early on with a question such as, “How many of you here know the results of the AFFIRM trial?” This allows you to make small alterations to meet the needs of your audience.
2. Visualize the stage and setting. Understanding the stage helps you anticipate and address barriers to learning. Imagine for a moment the difference in these two scenarios: a discussion of hyponatremia with a group of medical students at 4 p.m. in a dark room versus a discussion on principles of atrial fibrillation management at 11 a.m. in an auditorium. Both require interaction, although an auditorium-based presentation requires testing your audio-visual equipment in advance.
3. Determine your objectives. To determine your objectives, begin with the end in mind. If you were to visualize your audience members at the end of the talk, what would they know (knowledge), be able to do (behavior), or have a new outlook on (attitude)? The objectives will determine the content you deliver and the activities for learning. For a one-hour presentation, identifying three to five objectives is a good rule of thumb.
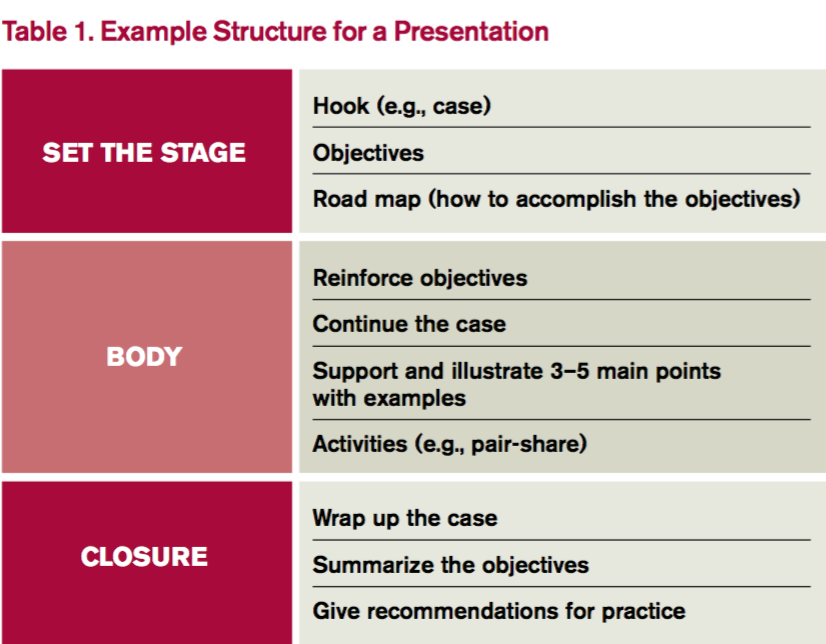
4. Build your presentation. Whether using PowerPoint, Prezi, or a white board, “build” the presentation from the objectives. Table 1 outlines one example format; Figure 1 outlines some best practices of PowerPoint.
Humans evolved to interpret visual imagery, not read text, so try to use pictures instead of bullet points. Consider first building slides with text and then using an internet search engine to convert words to pictures. For example, “atrial rate 200 bpm” is better displayed with an actual ECG.
5. Practice. Practicing helps you become more comfortable with the content itself as well as how to present that content. If you can, practice with a colleague and receive feedback to sharpen your material. No time to spare? Practice the introduction and any major point that you want to get across. Audiences decide within the first five minutes whether your talk is worth listening to before pulling out their cellphones to open up Facebook.
Delivery
1. Confront nervousness. Many of us become nervous when speaking in front of an audience. To address this, it’s perfectly reasonable to rehearse a presentation at home or in a quiet call room ahead of time. If you feel extremely nervous, breathe deeply for five- to 10-second intervals. During the presentation itself, find friendly or familiar faces in the audience and look them in the eyes as you speak. This eases nerves and improves your technique.

